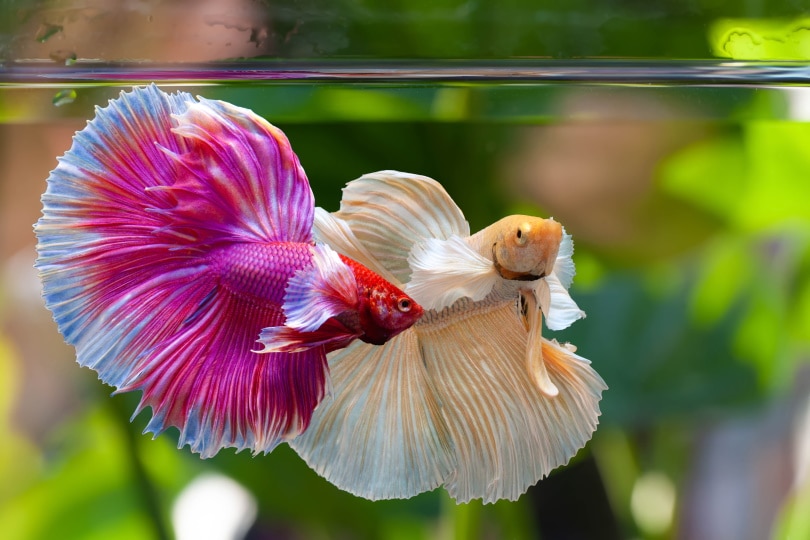
Bettas are popular aquarium fish, if just for their gorgeous colors. The species is native to Southeast Asia and has been introduced in several countries, including Columbia, Brazil, and the Dominican Republic. It’s primarily carnivorous, eating plankton, invertebrates, and insects in the wild. This information provides some vital clues for understanding how long a Betta can live without food.
Anecdotal evidence suggests they can survive between 10 to 14 days, though that certainly isn’t recommended. However, many variables exist associated with the species’ biology, stress response, and environmental conditions. Let’s explore how the Betta reacts when put under the ultimate challenge.
The Betta’s Evolutionary Adaptations to Stress
All organisms have the ability to manage stress to varying degrees. Nothing would be able to survive without this innate capacity. We can even go so far as to say all creatures need stress to adapt. Of course, it can take many forms, such as habitat loss, lack of water access, and a shortage of adequate food sources. That gives generalists who eat a wide variety of foods and live in variable niches an advantage.
In the wild, Bettas live in the rice paddies and other shallow waters of their native ranges in Southeast Asia. These areas also flood frequently. Thus, the fish evolved a unique ability to breathe air from the surface since the water conditions might be poor at times. It also suggests that washouts happen occasionally, which could affect food availability.
Bettas are called Siamese fighting fish for a good reason. The males will battle each other with little provocation, occasionally for hours, sometimes locking jaws. That provides further evidence of the species’ adaptation to stress, possible starvation, and extreme use of its energy resources. That ability also comes into play with feeding.
In the wild, Bettas consume mosquito larvae. Scientists have observed voracious eating. It’s worth noting that this pattern might be a feast-or-famine situation, with the time needed for the larvae to hatch between flooding events. This information also points to the Betta’s capacity to cope during times when food isn’t as readily available

The Ability to Cope
Usually, captive fish live longer than wild specimens, if just because of the lack of predation. A steady food supply is also critical. Therefore, it makes evolutionary sense that organisms would adapt to periods of low availability. That’s true even with fish like the Betta. The Siamese fighting fish might have an easier time with mosquito larvae and plankton. However, hunting success isn’t a done deal.
Carnivores, like the Betta, have an adaptive edge and can go longer between meals versus herbivores. After all, animal-based foods often take longer to digest than plants. The former are also nutrient-dense and can help meat eaters survive. Remember that seasonal variations are another driving force, allowing some fish to go months without eating.
Juvenile fish may not be able to go as long because of their high nutritional needs during development. Environmental factors may also play a role. Fish cope by shifting their metabolic processes. They’ll deplete energy stores or glycogen first from the liver. These chemicals are easy to digest. However, these reserves only go so far before the animal is forced to tap into its fat and protein sources.
If food deprivation continues, fish will no longer produce digestive enzymes to conserve energy. They’ll also become less active. The precise process varies with the species and other variables, including the Betta’s health. Fat breakdown becomes vital for supplying energy needs. Using protein from muscles occurs in advanced stages. Oxidative stress is also underway, further complicating matters.
Fish are superior to mammals in their coping ability. It’s worth mentioning that fish are cold-blooded animals or ectotherms. They don’t need to divert energy reserves toward maintaining their body temperature. That prolongs their ability to handle periods of low food availability better and longer than mammals.

The Betta Advantage
Captive Bettas also have a competitive edge over their wild counterparts. One study found that the latter produces higher levels of cortisol in response to the stress of a new environment. That effect can, in turn, interfere with a Betta’s foraging behavior, putting it at a greater risk of starvation and mortality. While wild fish can cope in these situations, captive Bettas have also evolved ways to handle this stress.
Final Thoughts
Bettas, like other fish, have adapted to environmental pressures. Food deprivation is a fact of life in the wild. The biology of fish helps them use their resources more efficiently to weather seasonal changes and climatic events. Your Siamese fighting fish has this ability, too, along with an excellent coping mechanism from captivity.
Featured Image Credit: panpilai paipa, Shutterstock